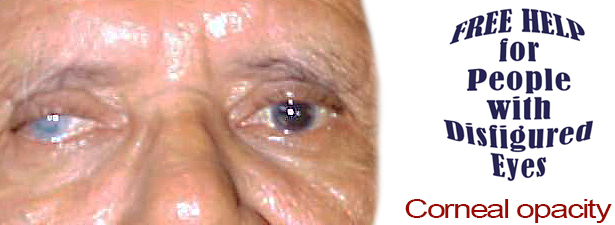
Corneal opacity is a disorder of the cornea, the transparent structure on the front of the eyeball, which can cause serious vision problems. Corneal opacity occurs when the cornea becomes scarred. This stops light from passing through the cornea to the retina and may cause the cornea to appear white or clouded over.
There are many causes of corneal opacity. In some cases, your eye care practitioner can recommend a treatment that will reverse the opacity and lessen your chance of needing additional treatment, such as surgery.
Causes: Infection, injury, or inflammation of the eye are the most common causes of corneal opacity.
Risk Factors
The following factors increase your chance of developing corneal opacity:
• Vitamin A deficiency
• Measles —when measles result in scarring/infection of the eye
• Foreign bodies striking the eye
• Eye injury, whether from a force, such as a poke in the eye, or from a chemical agent
• Herpes simplex virus —which can be transmitted to the eyes
• Other infections, including conjunctivitis
• Wearing contact lenses for a long period of time, especially overnight, can increase the risk of eye infections and also the chance of developing corneal opacity.